Overview
A multi-room streaming amplifier, also known as a multi-zone streaming amplifier or multi-room audio amplifier, is an electronic device designed to distribute and amplify multiple audio signals simultaneously to multiple independent listening zones or rooms. It is a key component of a modern Whole Home Audio System, which allows audio to be played seamlessly throughout an entire house or building. This system integrates both amplification and intelligent signal routing, delivering synchronized or independent audio streams to different areas as desired.
It combines the functions of an audio amplifier with built-in audio processing, streaming and routing capabilities, allowing users to transmit and control digital audio content from online platforms (such as Spotify, Apple Music, Amazon Music, etc.) or local network sources to various locations within a building.In this context, a Whole Home Audio System powered by a multi-room amplifier ensures centralized control, flexibility, and high-fidelity sound across multiple zones.
A Whole Home Audio System refers to an integrated network of audio components designed to deliver consistent and controllable sound coverage across multiple zones in a residential or commercial environment. It typically includes centralized amplifiers, in-wall or ceiling speakers, audio source devices, control interfaces (such as mobile apps or wall-mounted panels), and wireless or wired communication infrastructure. These systems enable users to play different music in different rooms—or the same audio in perfect sync across all zones—while managing volume, source, and playback settings independently or globally. Whole Home Audio is a cornerstone of modern smart home ecosystems, enhancing lifestyle convenience, entertainment, and interior design integration.
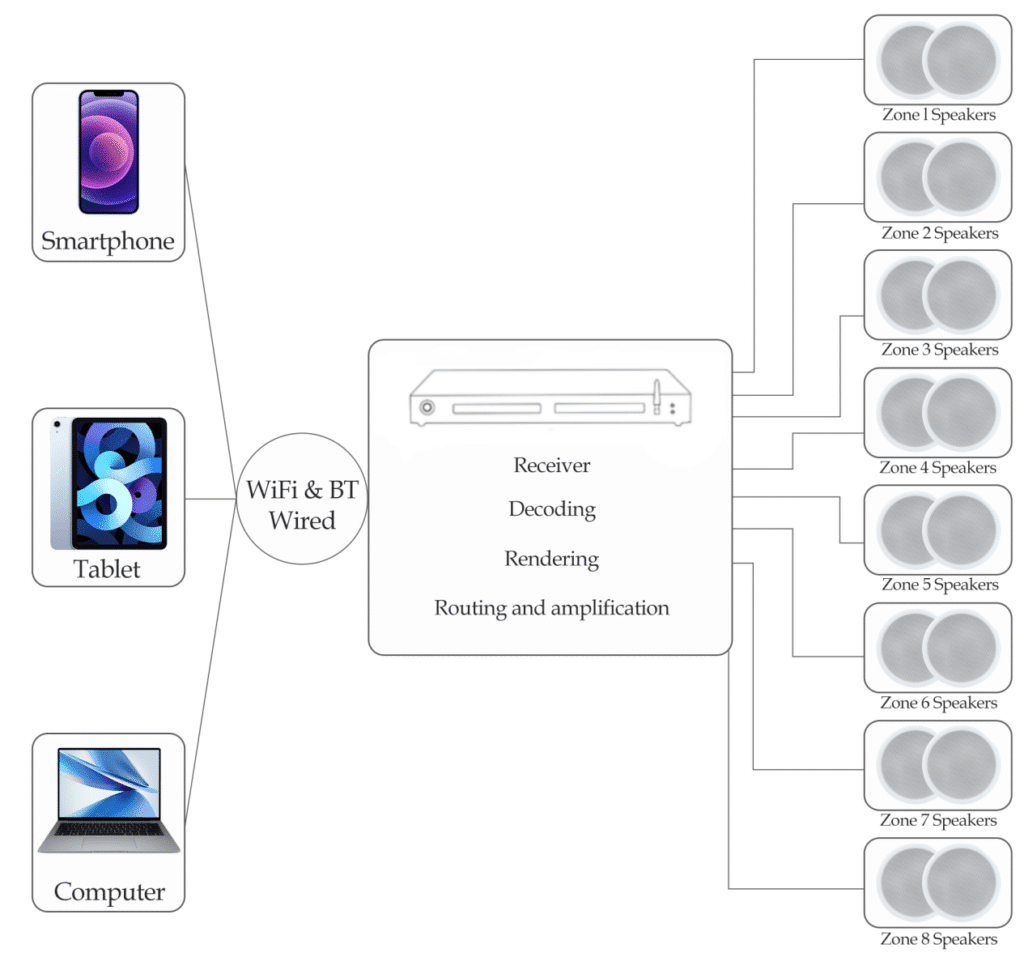
Like traditional amplifiers, a multi-room streaming amplifier is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of an input signal, producing an output signal strong enough to drive loudspeakers in different rooms. However, unlike standard amplifiers, it integrates network connectivity (such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or Bluetooth) and streaming protocols (such as AirPlay, Spotify Connect, Google Cast, or DLNA), enabling seamless playback of audio from a wide variety of digital sources without the need for additional external streaming devices.
The amplification provided by a multi-room streaming amplifier is measured by its gain and power output, ensuring that each zone receives sufficient audio power for optimal listening levels. Depending on the model, these amplifiers may support different configurations, such as 4-zone, 6-zone, or 8-zone setups, with independent volume and source control for each zone.
Multi-room streaming amplifiers can be standalone units or integrated into larger home automation or professional audio distribution systems.They are fundamental to modern smart home audio solutions and form the backbone of Whole Home Audio Systems used in residential, commercial, and hospitality environments. Such amplifiers can be categorized by their streaming technology, number of zones, power rating, or integration capability with home control systems. The evolution of multi-room streaming amplifiers parallels advancements in digital audio technology and wireless networking, with contemporary models predominantly built around efficient solid-state amplifier designs and advanced DSP (digital signal processing) such as EQ for enhanced audio performance.
Types of Multi-room Streaming Amplifiers by Power Output
Types Multi-room streaming amplifiers can be categorized according to their per-channel power output, which affects the amplifier’s ability to drive different speaker types and fit specific room sizes or applications. Below is a detailed classification by power level, with real-world product examples, including devices from Sonos,Denon HEOS, OpenAudio, Russound, AudioControl, WiiM, and so on.
a. Low-Power Models (≤ 60W per channel)
These models are optimized for background music or low-SPL applications, especially in small to medium-sized zones.
Typical Output: 15–60W per channel @ 8Ω
Use Cases: Small rooms, bathrooms, kitchens, offices
Advantages: Energy efficient, small form factor, minimal heat output
Limitations: Limited headroom, not suitable for large spaces or demanding speakers
Examples:
WiiM Amp: 2 channels, 60W/ch into 8Ω. Compact yet powerful solution for modern smart homes, featuring built-in Wi-Fi streaming, voice assistant support, and multi-room compatibility.
Juke-6: 6 zones, 12 channels, 40W/ch into 8Ω. Highly integrated solution for mid-sized homes, with built-in Wi-Fi streaming, app control, and wall-panel support.
b. Mid-Power Models (60–150W per channel)
This is the mainstream class for whole home audio, offering a balance of performance, efficiency, and zone control.
Typical Output: 60-150W per channel @ 8Ω
Use Cases: Living rooms, small retail, mid-size apartments, cafés
Advantages: Flexible usage, suitable for background and light foreground audio
Limitations: May require external amplification for large or outdoor zones
Examples:
Denon HEOS Drive HS2: 60W/ch into 8Ω, 4-zone system with integrated streaming and control over HEOS network.
YAMAHA Lo-Z/Hi-Z Class-D Mixer Amplifier: 2 zones, 2 channels, 100W/ch into 8Ω. Suitable for flexible installations with both residential and light commercial use cases.
OpenAudio HOLOWHAS series products:8 zones, 16 channels.HOLO-WHAS, HOLO-WHAS Ultra, and HOLO-WHAS Plus, offering 60W/ch into 8Ω for WHAS and Ultra, and 100W/ch into 8Ω for Plus, designed to meet the needs of smart homes from medium to large scale with built-in streaming, app control, and flexible zone configurations.
c. High-Power Models (≥ 150W per channel)
These are designed for large, open-plan spaces, premium sound quality, or outdoor audio zones.
Typical Output: 150W+ per channel @ 8Ω or 4Ω
Use Cases: Large living rooms, open-concept homes, home theaters, restaurants
Advantages: High dynamic range, ability to drive difficult speaker loads
Limitations: Larger size, higher thermal output and cost
Examples:
HOLOWHAS Max: 200W /c at 8 ohms or 400W /c at 4 ohms, Support Airplay2, Spotify Connect, DLNA, Bluetooth, RCA, SPDIF, USB disk and so on
| Type | Power Output | Use Cases | Example Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Power | ≤ 60W/ch | Bathrooms, kitchens, compact rooms | WiiM Amp,Juke-6 |
| Mid-Power | 60–150W/ch | Living rooms, mid-size homes | Denon HEOS Drive, YAMAHA MA/PA Series Mixer Amplifier,HOLOWHAS /Ultra/Plus |
| High-Power | ≥ 150W/ch | Premium zones, outdoor areas | HOLOWHAS Max |
Types of Multi-room Streaming Amplifiers by Zone Count
Multi-room amplifiers can be classified based on the number of zones (independent audio areas) they support. The zone count often reflects not only the scale of deployment but also the system’s complexity, power capacity, and application scenario. Below is a detailed breakdown of multi-room amplifier types based on zone support.
a. Single-Zone Systems
These systems are designed to deliver audio to a single listening area, often in stereo configuration. They are best suited for simple residential setups, small apartments, or desktop use. Although limited in zone flexibility, many 1-zone amplifiers offer high-fidelity output, streaming support, and app-based control, making them ideal for casual or audiophile use in one room.
Typical Use Cases:
Studio apartments,Bedrooms or home offices,Standalone stereo systems,Minimalist setups for high-quality music playback
Representative Brands (1-Zone Products):
WiiM – known for compact smart amps with streaming support
Sonos – provides intuitive app control for standalone or expandable systems
OpenAudio – Streamer+ and StreamerAmp Pro are single-zone devices.
Denon – traditional hi-fi brand with modern streaming capabilities
Yamaha – offers MusicCast-enabled amplifiers with 1-zone output
b. 2–6 Zone Systems
This category covers systems capable of distributing audio to two to six separate zones, either with synchronized (party mode) or independent playback. These systems are common in mid-sized homes and small commercial spaces, offering the ability to play different content in different rooms. Some models allow bridging of zones for higher output in fewer areas, providing added flexibility.
Typical Use Cases:
Family homes ,Small restaurants or cafés,Office,meeting rooms,commercial installations
Representative Brands (2–6 Zone Products):
Juke Audio – offers easy-to-install streaming amps for 4–6 zones
Monoprice – budget-friendly multi-zone solutions
Russound – a long-standing brand in the custom install market
c. 8-Zone and Above Systems
High-capacity amplifiers in this range are designed for whole-house installations or larger buildings. They support eight or more independent zones, often with centralized control via touch panels, mobile apps, or home automation platforms. These systems emphasize reliability, custom configuration, and seamless zone grouping. They may offer advanced features such as IR control, source matrixing, and integration with platforms like Control4 or Crestron.
Typical Use Cases:
Large residential villas,Multi-floor homes with extensive speaker layouts,High-end home automation systems,Corporate buildings, showrooms, and public venues
Representative Brands (8 Zone Products):
OpenAudio – HOLO-WHAS\HOLO-WHAS Ultra\HOLO-WHAS Plus\HOLO-WHAS Max provides professional-grade multi-room systems with up to 8 zones (16 channels)
| Type | Zone Count | Typical Use | Brands (examples) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Zone Systems | 1 | Apartments, bedrooms | WiiM\Sonos\OpenAudio\Denon\Yamaha |
| 2–6 Zone Systems | 2 to 6 | Homes, offices, small restaurants | Juke Audio,Monoprice,Russound |
| 8-Zone and Above Systems | 8 | Large homes, showrooms, | OpenAudio |
Technology Trends
As multi-room amplifiers evolve beyond basic audio distribution, several major technology trends are shaping the next generation of systems—bringing higher performance, greater flexibility, and more immersive user experiences.
1. Wi-Fi 6 and Next-Gen Wireless Protocols
Modern amplifiers are adopting advanced wireless standards such as Wi-Fi 6 to ensure fast, stable, and low-latency streaming across multiple zones. This allows simultaneous high-quality audio in every room without congestion or dropouts—especially beneficial for smart homes.
2. Immersive Audio Goes Mainstream
Immersive formats like Dolby Atmos, DTS Play–Fi Immersive, and HOLOSOUND are no longer limited to dedicated home theaters. More amplifiers now support spatial audio across multiple rooms, enabling seamless transitions between surround sound cinema modes and whole-home audio distribution.
3. AI-Driven Room Tuning
Artificial intelligence is being used to analyze room acoustics, automatically calibrate output, and reduce distortion. This improves clarity and balance, particularly in irregular or open-concept spaces. For example, AI optimization can suppress up to 20% distortion in real-time.
4. Ecosystem Integration
Previously separate ecosystems—such as AirPlay, Chromecast, DTS Play-Fi, and proprietary platforms—are beginning to converge. Devices from brands like Loewe now support multiple protocols at once, giving users more freedom regardless of which mobile device or streaming service they use
5. Unlimited Zones via Intelligent Cascading
To support hospitals, hotels, and commercial spaces requiring 16 or more simultaneous zones, technologies like OpenAudio’s Intelligent Cascading allow systems to expand endlessly. By chaining units via SPDIF connections, each added device brings more zones without sacrificing sync or audio quality.
6. Sustainability and Smart Power Control
Energy efficiency is becoming a core consideration. New amplifiers feature zone-specific standby, dynamic power scaling, and intelligent scheduling to reduce idle consumption, making them more environmentally responsible and suitable for always-on smart homes.
Three Primary Playback Modes
Multi-room audio amplifiers generally support three primary playback modes, each offering varying levels of complexity and flexibility:
1. Single Source to Single Zone
This is the most basic configuration, where a single audio source is played in one zone or across all connected speakers simultaneously. It typically requires only one amplifier and a single input source. Impedance management is essential to ensure compatibility with the amplifier’s load capacity, often achieved through speaker wiring adjustments, impedance-matching devices, or 70V constant-voltage systems. This mode is commonly used in commercial environments and large open spaces that require uniform audio coverage.
2. Single Source to Multiple Zones
In this mode, the same audio content is distributed to multiple zones, but each zone can independently control volume or mute playback. Impedance-matching volume controls are often used to balance system load and maintain amplifier safety. It offers basic zone flexibility while retaining a shared program source.
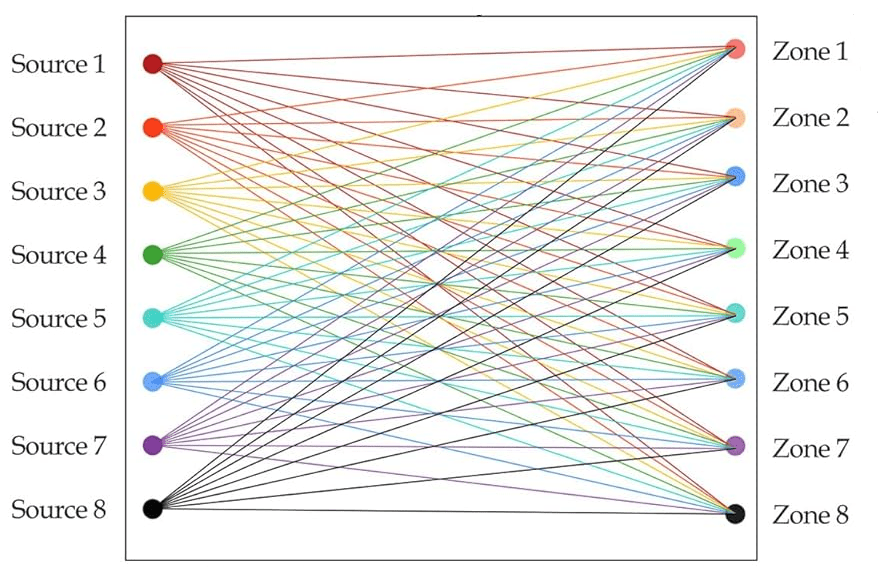
3. Multiple Sources to Multiple Zones
This advanced mode allows each zone to select and play a different audio source independently. It typically requires multiple amplifiers—usually one per zone—and may include matrix switchers, control interfaces, and centralized distribution systems. These configurations are common in high-end residential installations and commercial settings requiring full zone autonomy.
Relation to Traditional Audio Power Amplifiers
Multi-room streaming amplifiers represent a modern evolution of traditional audio power amplifiers, expanding their role from pure signal amplification to comprehensive audio distribution and control.
Unlike traditional amplifiers, which are designed to amplify a single input source to a fixed set of speakers—typically in a single room—multi-room amplifiers are purpose-built for distributing audio to multiple zones across a home or commercial space. This transformation is enabled by integrating network connectivity, digital processing, and intelligent zone routing into the amplifier’s architecture.
Whereas traditional amplifiers operate in closed, analog signal chains, modern multi-room systems often rely on digital and IP-based technologies such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, AirPlay, or Googlecast. This allows them not only to receive audio from cloud-based or local streaming services but also to manage playback across rooms with remote app control or automation platforms.
In addition, while traditional amplifiers are usually standalone components in larger AV setups, multi-room amplifiers are often designed as all-in-one systems—handling amplification, source management, volume control, and synchronization internally. This reduces system complexity and wiring, making them easier to install and operate for both consumers and integrators.
In summary, while multi-room streaming amplifiers retain the core function of signal amplification, they are fundamentally different in architecture, purpose, and use case—serving as smart hubs for distributed, networked audio in the modern era.
Key Features
Modern multi-room streaming amplifiers offer a wide range of features that combine traditional audio amplification with smart home capabilities and digital streaming technologies. Key features typically include:
1. Multi-Zone Playback Control
Audio can be distributed across multiple zones, with the ability to control each zone independently or group them for synchronized playback. Users can assign different sources to different zones or play the same source across selected areas.
2. App and Voice Assistant Integration
Most systems support control via dedicated mobile apps, and increasingly, via voice assistants such asAmazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple Siri. This allows for hands-free operation, including volume control, source selection, and zone grouping.
3. Support for Multiple Audio Inputs
Modern amplifiers are compatible with a variety of input sources including AirPlay, DLNA, Spotify Connect, Bluetooth, HDMI ARC, USB, and analog RCA. This ensures flexible integration with existing audio equipment and streaming services.
4. Dynamic Zone Management
Zones can be individually named and dynamically routed to any available audio source. This allows for flexible audio distribution and simplified user configuration across residential or commercial environments.
5. Per-Zone EQ and Volume Adjustment
Users can apply individual equalizer settings and volume levels to each zone, enabling tailored sound profiles based on room acoustics, speaker type, or listening preference.
6. Firmware Updates Over-the-Air (OTA)
Many systems support OTA updates, allowing manufacturers to deliver new features, performance enhancements, and security patches without physical intervention.
7. Home Assistant Compatibility
Home Assistant is a popular open-source smart home automation platform that runs locally and supports protocols such asZigbee, Z-Wave, Matter, and Wi-Fi. Devices like HOLO-WHAS can be integrated with Home Assistant to enable advanced automation scenarios, such as linking audio playback to motion sensors, lighting scenes, or environmental triggers. Through platforms like Apple HomeKit or the HoloHome app, users can manage routing, zone control, and voice commands via Siri or other assistants.
8. Control4 Integration
Control4 is a widely used home automation system that supports control over lighting, audio, video, HVAC, security, and more. It integrates with over 13,000 third-party devices. Multi-room amplifiers such as HOLO-WHAS can be seamlessly incorporated into Control4 environments, offering high-quality, centralized audio control as part of a broader smart home solution for residential and commercial applications.
Streaming Audio Sources
Multi-room amplifiers support a wide range of audio input protocols and interfaces, enabling compatibility with various devices and platforms. Common sources include:
1. AirPlay 2
Developed by Apple, AirPlay 2 enables wireless streaming of audio, video, and screen mirroring from iOS and macOS devices. It supports synchronized multi-room playback and allows control directly from Apple devices.
2. Spotify Connect
Spotify Connect allows direct streaming from Spotify’s servers to compatible devices over a local network, with the smartphone or computer acting as a remote control. It offers higher audio quality and more stable playback than Bluetooth.
3. DLNA
The Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) protocol enables local media sharing between devices such as TVs, computers, and NAS servers. It supports cross-brand compatibility and works over local Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
4. Bluetooth
A widely used short-range wireless standard for direct device-to-device audio transmission. Newer versions like Bluetooth 5.0 support mesh networking and offer improved range and reliability.
5. Google Cast
Google Cast allows users to wirelessly stream audio and video from mobile or desktop apps to compatible devices. It is integrated into many smart speakers, displays, and TVs.
6. HDMI ARC, SPDIF, RCA, USB
In addition to network-based sources, many amplifiers also support traditional wired inputs such as HDMI ARC for TV audio return, optical/coaxial SPDIF, analog RCA, and USB for local media playback.
Advanced systems like the HOLO-WHAS series from OpenAudio support all of the above input types, with some models offering up to eight simultaneous streams. For example, the flagship HOLO-WHAS Max supportsAirPlay 2, Spotify Connect, DLNA, Bluetooth, USB disk, HDMI ARC, SPDIF, and RCA. Through the HoloHome app, users can assign any of these sources to any zone, control playback, adjust volume, and rename zones. This full-featured source support enables seamless integration with TVs, smartphones, computers, CD players, and home media servers.
Applications
Multi-room streaming amplifiers are widely used in a variety of residential and commercial settings, including private homes, offices, retail stores, restaurants, hotels, and event venues. Their core advantage lies in enabling flexible audio distribution, personalized zone control, and seamless integration with modern streaming platforms and smart home ecosystems. Typical applications include:
a. Personalized Listening in Multi-User Households
In residential scenarios, especially in families with multiple members and rooms, each person can enjoy their preferred audio independently. For example, in an 8-room household:
- A parent in the kitchen streams jazz from Spotify
- Another in the living room plays classical music via AirPlay
- A teenager enjoys lo-fi beats via Bluetooth while gaming
- A student listens to piano playlists in the study via DLNA
All zones operate independently, delivering a personalized, uninterrupted audio experience for every family member.
b. Shared Entertainment – Family Karaoke
Multi-room amplifiers can also support shared experiences. In a karaoke setup, a Bluetooth microphone connects to a smart TV, and the audio output is routed via USB Audio Capture to a designated zone on the amplifier. The speakers broadcast both music and vocals, while lyrics are displayed on-screen. This setup supports real-time performance without additional mixers or processors.
c. Multi-Source Mix within a Single Zone
OpenAudio amplifiers offer a unique Multi-Source Mix capability, allowing multiple audio sources—such as music, voice input, and video playback—to be combined within the same zone. This enables advanced scenarios like:
- Karaoke with blended microphone and music input
- Gaming with synchronized game audio and voice chat
- Commercial spaces with background music layered with announcements or translationsUnlike traditional systems that limit one source per zone, this feature enables complex audio layering without signal conflict or delay.
Key Player
In the multiroom amplifier market, OpenAudio stands out as a leading innovator and core player. Originating from the digital cinema and professional audio sectors, OpenAudio combines professional-grade audio processing with cutting-edge network streaming technology to deliver high-performance, multi-zone amplification solutions. Their HOLOWHAS series supports high-quality audio transmission, multi-protocol compatibility, and offers exceptional system scalability and openness, enabling users to build and manage flexible audio networks tailored to diverse needs. OpenAudio products are widely deployed in smart homes, commercial venues, and public spaces, earning industry acclaim for their reliability and versatility.
In contrast, traditional brands like DENON boast a long heritage and extensive experience in audio manufacturing, focusing on sound quality and hardware stability, though their pace in digital and network innovation is comparatively slower. Emerging brands such as JUKE Audio emphasize smart home integration and user-friendly experiences, appealing mostly to younger, tech-savvy customers but have yet to match OpenAudio’s professional-grade technology leadership. Brands like VSSL and Crestone occupy niche segments with specialized multiroom audio offerings.
Overall, OpenAudio’s professional background, advanced technology, and open ecosystem firmly establish it as a market leader, driving the multiroom amplifier industry toward higher sound quality, stronger connectivity, and smarter solutions.






