Whole-Home Audio ≠ Surround Sound
Many people struggle to clearly separate Whole-Home Audio (WHA) from Surround Sound, so their plans get messy. Some buy a surround-sound receiver only to discover it can’t drive speakers in every room, while others pick up a multi-room streaming amp and then ask the manufacturer to add surround features—like the subwoofer support we talked about in earlier posts. Bottom line: we need to spell out that these are two completely different animals.
Don’t mix them up—here’s the quick-and-dirty difference:
Surround Sound
Surround sound refers to the way in which sound is distributed within a single room, typically for the purpose of matching the audio to a video source displayed on a screen—think “home theater” and “media rooms”—although it is not uncommon for master bedrooms and other rooms in the house to be set up with surround sound. Whereas surround sound requires a home theater receiver for processing video and audio in multiple formats (e.g. Dolby Digital, Dolby Atmos, DTS, Auro-3D, etc.)
Here’s a quick rundown of Surround Sound’s main features:
- One room, one screen.
- Purpose: make the audio track of a movie or game wrap around you.
- Gear: AV receiver decoding Dolby Digital, Dolby Atmos, OpenAudio HoloSound, DTS:X, etc.
- Typical spots: home theaters, media rooms, sometimes a tricked-out master bedroom.
Typical Surround sound span from 2D such as (5.1, 7.1) to 3D (5.1.2, 7.1.4, 9.1.6, etc).
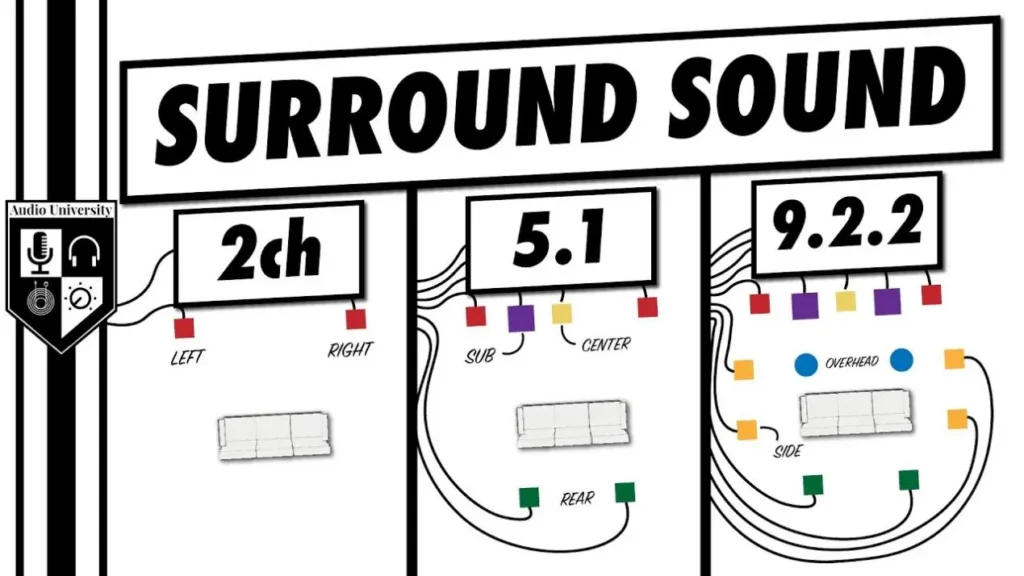
To dive deeper, check out our primers on immersive audio:What’s Immersive Audio
and the roles of DCI and SMPTE:DCI Digital Cinema Standards and SMPTE Immersive Audio Standards: Shaping the Future of Cinematic Experiences.
Whole-Home Audio (WHA)
WHA refers to the distribution of stereo audio throughout the home. a whole-house audio system requires equipment that manages what audio source is heard, and at what volume, within each zone. Here’s a quick rundown of WHA’s main features:
- Music everywhere.
- Purpose: pump any source—Spotify playlist, vinyl, doorbell chime—into any room, at whatever volume you want.
- Gear: a matrix switch or amp that routes stereo audio to multiple “zones” (kitchen, patio, study…).
- No video processing needed—just clean, synced sound that follows you from the coffee maker to the couch.
For a deeper look at multi-room streaming amplifier setups, check out our earlier article:Multi-Room Streaming Amplifier
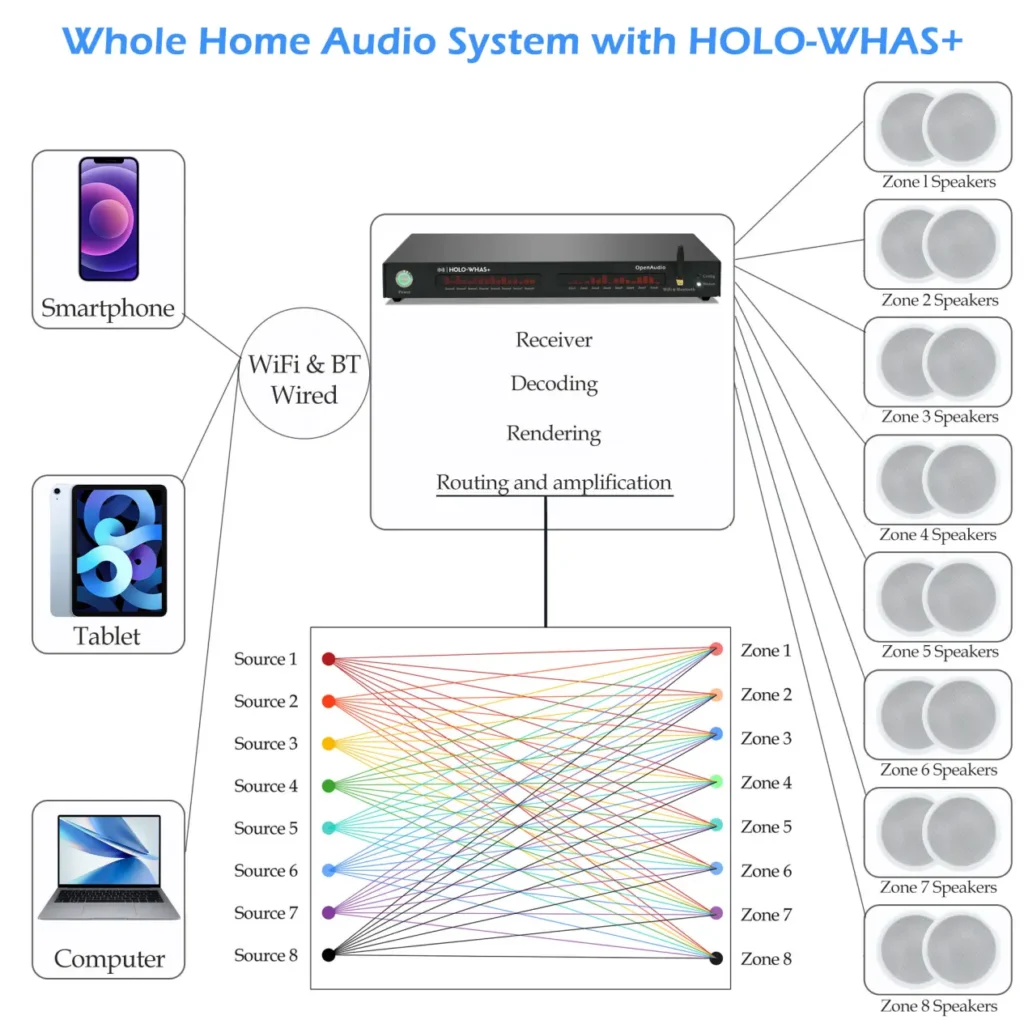
Is It possible to build one “monster” system that crushes both surround sound and whole-home audio
OpenAudio’s next drop—the AVR-16200—brings the thunder on both fronts.
• Surround Sound? Dolby Atmos 9.1.6, maxed out.
• Whole-Home Audio? Nine killer advantages that leave the competition in the dust.
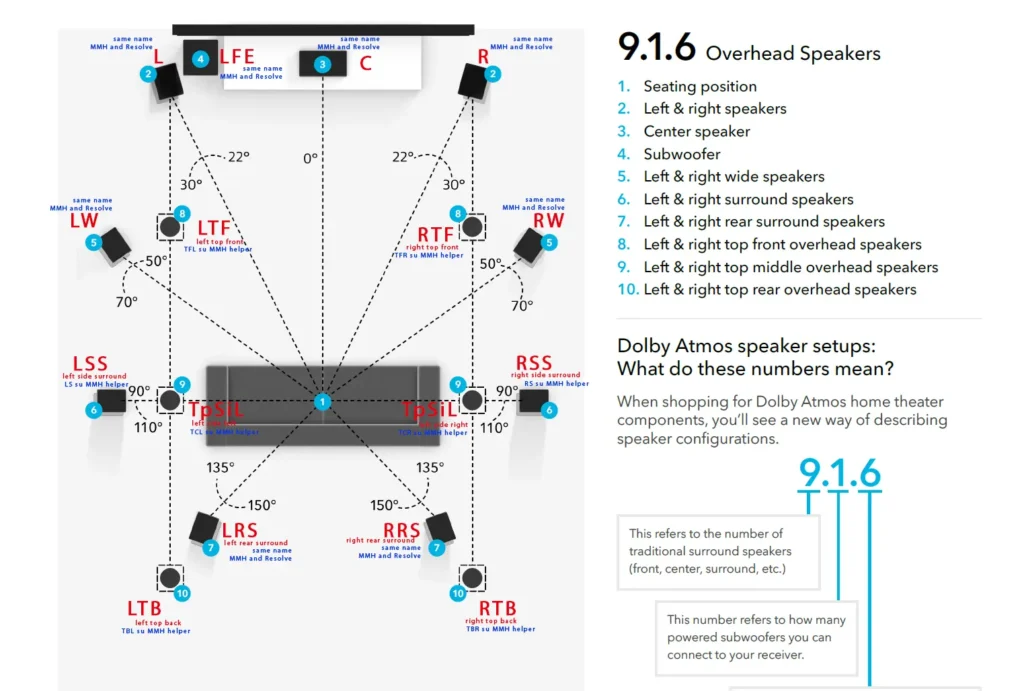
The 9.1.6 Configuration include Left & Right Speaker, Center Speaker, Subwoofer, Left & Right Wide Speaker, Left & Right rear surround speaker, Left & Right top front overhead speaker, Left & Right top middle overhead speaker, Left & right top rear overhead speaker.
Surround Sound Configurations Comparison Table
The nine killer advantages include: Multiple-Zone Amplifier, Multiple Input formats, Superior Routing Capability, Exceptional DSP Processing, Full WebAPI can Control4, Flexible and Unified App, Support up to 8 inputs, and Any music platform, and unmatched Power output.

You can run the AVR-16200 in full surround sound mode, whole-home audio mode — or blend both for the best of both worlds.
| SRS | WHA | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 8 zones |
| 2 | 2.1 | 6 zones |
| 3 | 5.1 | 5 zones |
| 4 | 7.1 | 4 zones |
| 5 | 5.1.2 | 4 zones |
| 6 | 7.1.2 | 3 zones |
| 7 | 5.1.4 | 3 zones |
| 8 | 7.1.4 | 2 zones |
| 9 | 9.1.4 | 1 zone |
| 10 | 9.1.6 | 0 zone |
Notes: 1 (subwoofer) can use line out interface of AVR-16200 with correct EQ setting.







